By age 50, you’ve likely lost up to 10% of your muscle mass, and your bones are becoming more porous with each passing year—but your fork holds more power than you think.
You’re feeling it already. Carrying groceries feels harder. You worry about falling. Your body takes longer to bounce back after exercise.
And the nutrition advice out there? It’s a mess of contradictions.
Here’s what you need: real foods that protect both your muscles and bones.
This article shows you 11 scientifically-proven foods for muscle mass and bone density. You’ll learn exactly how each one works in your body.
We’ll cover simple serving sizes you can start using today. You’ll discover which Foods for Maintaining Muscle Mass and Bone Density pack the biggest punch.
And you’ll see why combining certain foods builds strong bones and muscles faster than eating them alone.
No confusion. Just clear answers you can use right now.
🥗 11 Foods That Build Strong Muscles & Bones After 40
Science-backed nutrition for lifelong strength
💪 Your fork holds more power than you think. The right foods protect both muscles and bones simultaneously.
👆 Click to explore the complete guide

Why Muscle Mass and Bone Density Matter After 40
Your body starts breaking down faster than it builds up. After 30, you lose 3-8% of your muscle every ten years. Once you hit 60, that speed doubles.
The 2023 NIH reports that nearly 45% of adults over 60 show signs of age-related muscle loss.
Your bones thin out too. One in two women and one in four men over 50 will break a bone from weak bones. That’s not just a statistic. It’s your independence at risk.
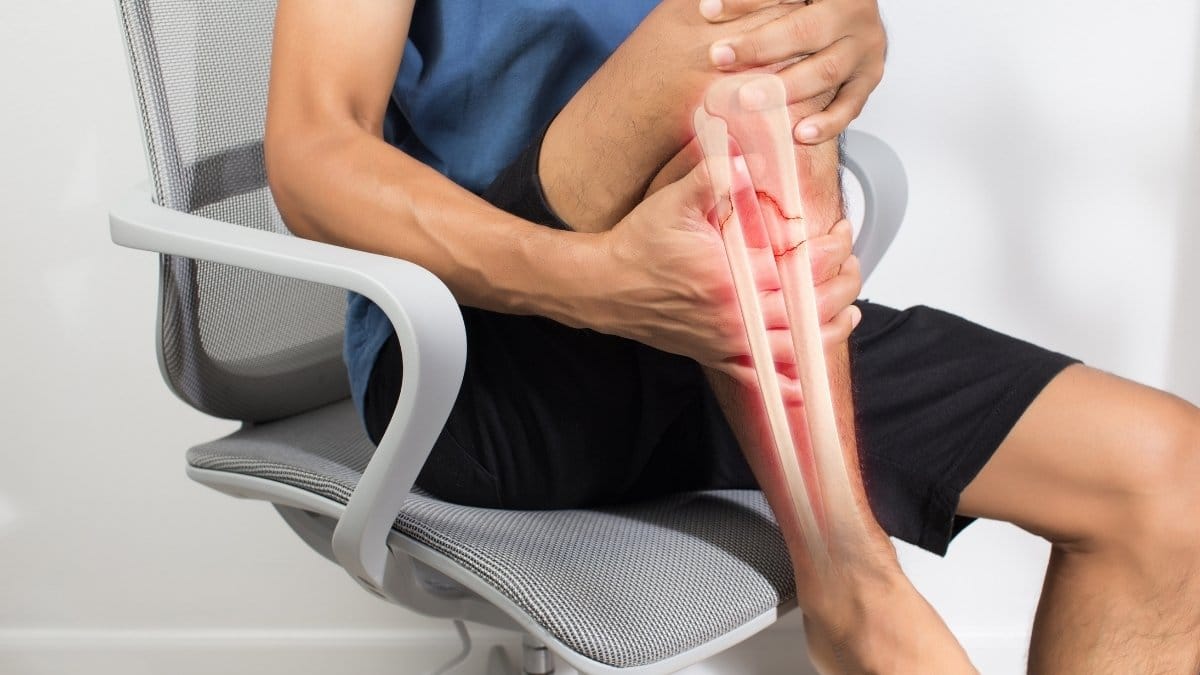
Here’s what most people miss: your muscles and bones work together. When your muscles contract, they pull on your bones.
This pulling tells your bones to stay strong and build new tissue. Less muscle means weaker bones.
The real-world cost is steep. Falls lead to fractures. Fractures steal your freedom. Your metabolism drops 8% every decade as muscle disappears.
Maintaining muscle mass protects both systems at once.
And here’s the surprise: 50% of your bone strength comes from protein, not calcium alone. Diet matters more than you’ve been told. Bone density depends on what you eat every single day.
1. Greek Yogurt: The Protein-Calcium Powerhouse

One cup of Greek yogurt delivers 15-20g of protein—triple what regular yogurt gives you. It contains both whey and casein proteins.
Whey works fast. Casein releases slowly over hours. This combo keeps feeding your muscles all morning long.
Greek yogurt ranks among the best protein-rich foods and calcium foods you can eat. One serving covers 20% of your daily calcium needs.
Your body absorbs this calcium easily, unlike some supplements that pass right through you.
Here’s the comparison: Regular yogurt has 5-7g protein. Milk has 8g. Greek yogurt wins by a mile.
The 2022 Journal of Nutrition found that postmenopausal women who ate yogurt daily had stronger bones than those who didn’t.
The probiotics inside help your gut absorb more nutrients from everything you eat.

Most brands add vitamin D, which helps your body grab onto that calcium.
The leucine inside triggers something called the mTOR pathway. Think of it as flipping the “build muscle” switch in your cells.
Eat it in breakfast bowls. Blend it in smoothies. Use it as a base for savory dips.
2. Salmon: Omega-3s Meet Vitamin D
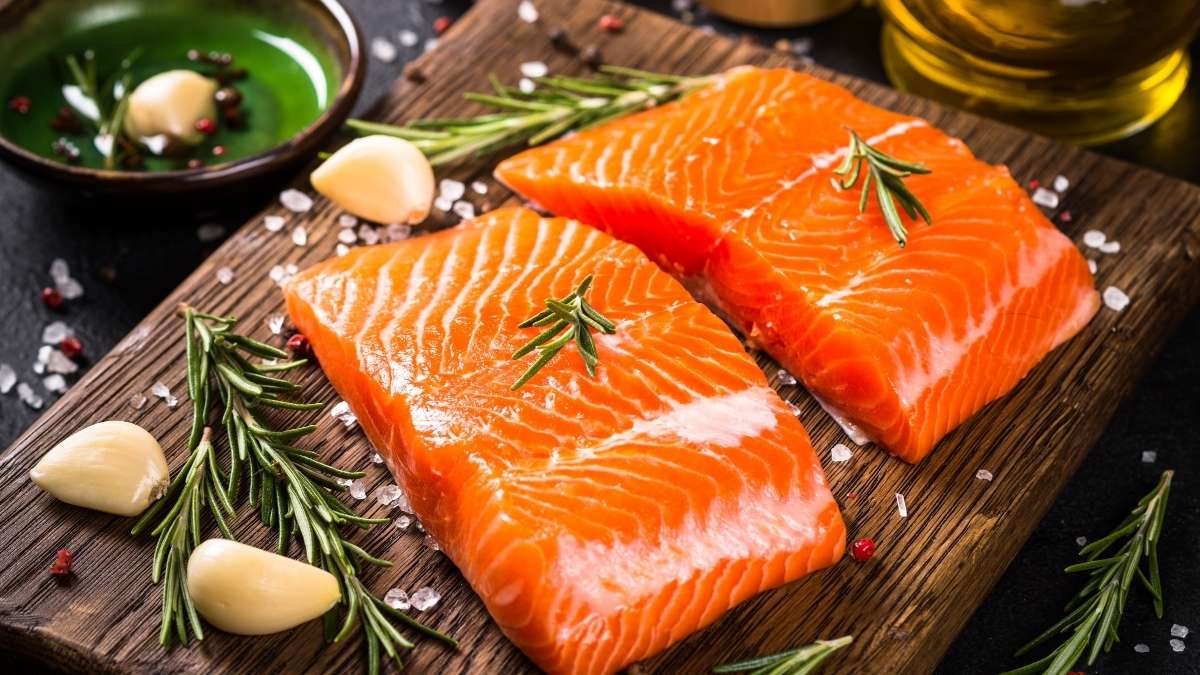

A 3-ounce piece of salmon packs 22g of complete protein plus 450mg of omega-3 fatty acids. Those omega-3s calm down inflammation in your body.
Less inflammation means your muscles recover faster after exercise or daily activities.
Salmon stands out as one of the rare vitamin D foods found in nature. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that vitamin D boosts calcium absorption by 30-40%.
Without enough vitamin D, your body wastes the calcium you eat. It’s like trying to build a house without nails to hold the boards together.
The selenium in salmon protects your cells while they repair muscle tissue. Wild salmon contains slightly more omega-3s than farmed, but both work as foods for strong bones.
Aim for 2-3 servings of salmon each week. That’s roughly twice a week at dinner. Bake it, grill it, or pan-sear it with lemon.

Can’t eat fish? Look for fortified orange juice, cereals, or talk to your doctor about vitamin D supplements. Your bones need this vitamin either way.
3. Eggs: Nature’s Muscle-Building Package
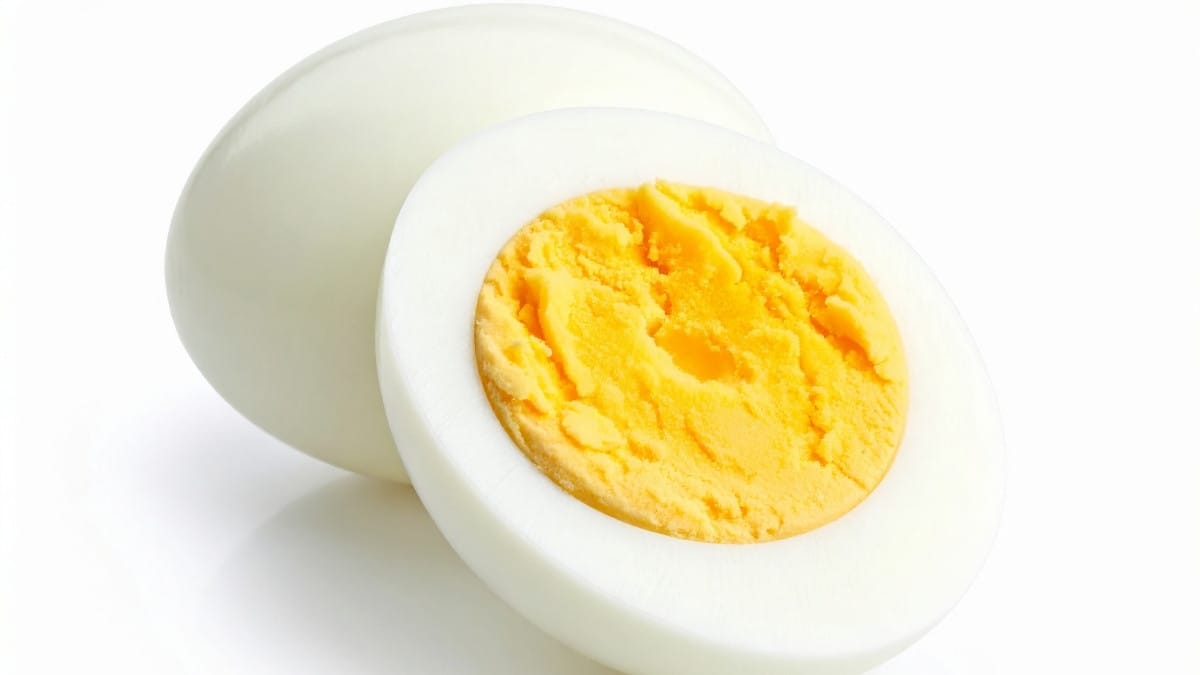

Eggs score a perfect 100 for protein quality—the gold standard. Each egg gives you 6g of protein that your body absorbs and uses easily.
Scientists rate eggs as the best protein source for muscle maintenance because they contain every amino acid your muscles need.
The yolk is where the magic happens for your bones. It contains vitamin D and vitamin K2, which tells your body to put calcium in your bones, not your arteries.
Most people throw out the yolk. Big mistake.
Eggs are loaded with leucine, which flips on muscle building in your cells. The choline inside keeps the nerves that control your muscles working right.
The 2024 dietary guidelines cleared eggs—cholesterol from food doesn’t raise your blood cholesterol like we once thought.

Eat the whole egg. Post-workout eggs help your muscles recover fastest.
These protein-rich foods for muscle maintenance cost pennies per serving.
4. Leafy Greens: The Overlooked Bone Builders

Most people think dairy is the only calcium source, but kale and collard greens beat milk for absorption.
Your body absorbs 40-50% of calcium from kale compared to just 32% from dairy. That’s nearly 50% more calcium going into your bones.
Leafy greens contain vitamin K1, which activates a protein called osteocalcin. This protein acts like glue, binding calcium to your bone structure.
The Rotterdam Study tracked 4,800 people and found that those who ate the most vitamin K had 30% fewer fractures.

These greens also pack magnesium, which turns vitamin D into its active form.
Without magnesium, that vitamin D you’re taking sits useless in your body. Folate in these vegetables helps rebuild muscle cells after they break down.
Focus on kale, collards, spinach, and bok choy. Lightly cook them—heat breaks down the cell walls and releases more calcium.
Steaming for 3-5 minutes works perfectly. These calcium and vitamin D foods belong on your plate daily.
5. Lean Beef: Bioavailable Protein and Minerals
A 3-ounce serving of lean beef delivers 25g of complete protein—all the amino acids your body needs for maintaining muscle mass.

The International Osteoporosis Foundation recommends 1-1.2g of protein per kilogram of body weight daily. A palm-sized piece of beef gets you halfway there in one meal.
Beef contains heme iron, which your body absorbs three times better than iron from plants. This iron carries oxygen to your muscles so they work efficiently.
The zinc in beef repairs muscle tissue and supports healthy testosterone levels, which decline as you age.
Here’s a bonus: beef naturally contains creatine. Your muscles use creatine for quick bursts of strength. Most people only get creatine from supplements, but beef gives it to you in food form.
Grass-fed beef has slightly more omega-3s than grain-fed, but both work as protein-rich foods. Vitamin B12 keeps your nerves firing and builds red blood cells.
6. Almonds: Plant-Based Bone Support

A quarter cup of almonds gives you 6g of protein plus healthy fats that help absorb vitamins.
But the real power is in the magnesium—76mg per ounce. Your body needs magnesium to convert vitamin D into its active, usable form. Without it, that vitamin D supplement you’re taking doesn’t work.
The NIH found that people with higher magnesium intake had significantly denser bones.
Almonds also contain phosphorus, which teams up with calcium to build bone tissue. Think of calcium as bricks and phosphorus as the cement holding them together.
Vitamin E in almonds fights cell damage during muscle recovery.
The prebiotic fiber feeds good gut bacteria, which improves how well you absorb minerals from all foods for strong bones and muscles.
Almond butter works just as well—spread two tablespoons on toast. Stick to 1-1.5 ounces daily. That’s about 23 almonds. More isn’t better—almonds are calorie-dense.
7. Cottage Cheese: Slow-Release Muscle Fuel

One cup of low-fat cottage cheese packs 28g of casein protein—the slow-digesting type that feeds your muscles for hours.
While whey protein from Greek yogurt works fast, casein releases amino acids gradually. This makes cottage cheese perfect before bed.
The British Journal of Nutrition found that people who ate protein before sleep built more muscle overnight.
Your body repairs itself while you sleep, and casein keeps the building blocks available all night long.
Cottage cheese contains phosphorus, which works with calcium to harden your bones. The selenium inside supports your thyroid gland,
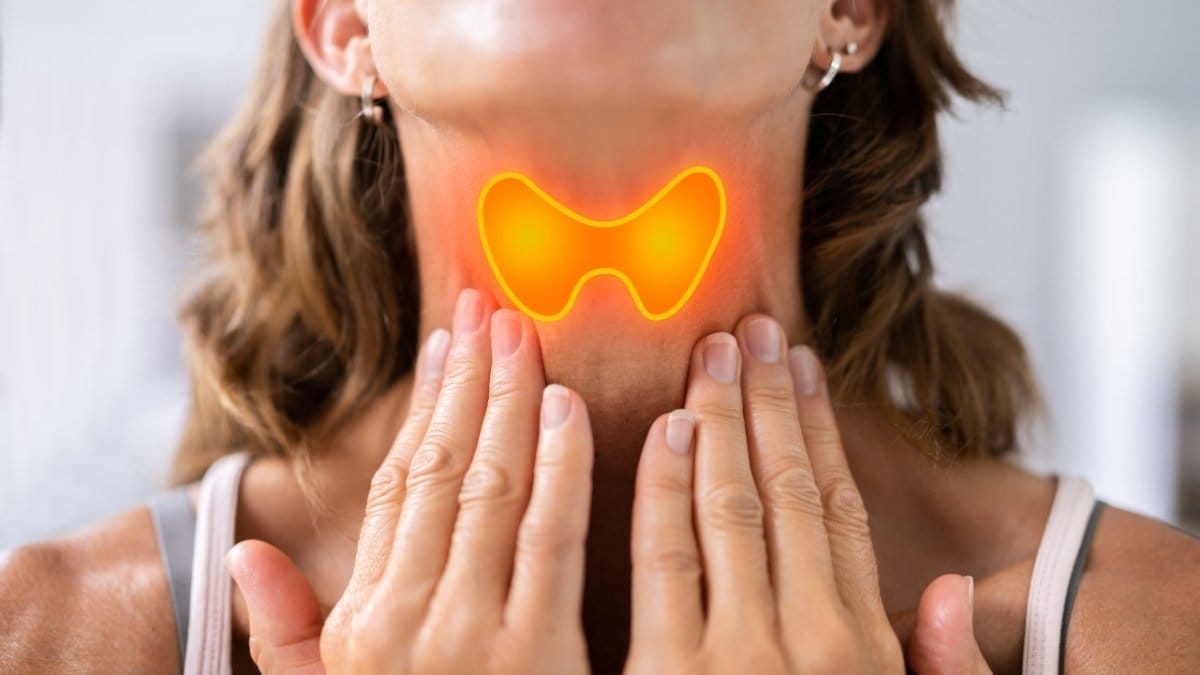
which controls your metabolism and muscle function. A sluggish thyroid means weak, tired muscles.
These protein-rich foods for muscle maintenance come in low-sodium versions if you’re watching salt intake. Eat it sweet with berries and honey.
Or go savory with tomatoes, cucumbers, and pepper. Either way, you’re getting quality fuel for maintaining muscle mass.
8. Sardines: Small Fish, Big Impact

You eat sardines bones and all—that’s 325mg of pure calcium per 3-ounce serving.
The bones are soft and completely edible. They also deliver 250+ IU of vitamin D, matching what you’d get from a supplement pill.
These calcium and vitamin D foods for bone health come in a tiny, affordable package.
Sardines cost a fraction of salmon but deliver similar nutrition. You get 22g of complete protein plus omega-3 fatty acids that calm muscle inflammation as you age.
Studies of Mediterranean populations show that people who eat small fish regularly have stronger bones and fewer fractures.

Sardines are sustainable and low in mercury because they’re small and don’t live long enough to accumulate toxins.
Toss them on salads. Mash them on whole-grain toast with lemon. Mix them into pasta with garlic and olive oil.
One can gives you a full serving. Keep them in your pantry for quick meals.
9. Sweet Potatoes: Carbs That Build Strength

One medium sweet potato contains 542mg of potassium, which stops your body from flushing calcium out through urine.
The Journal of Bone and Mineral Research found that people with higher potassium intake lost significantly less calcium and had denser bones.
Your kidneys literally hold onto more calcium when you eat enough potassium.
Sweet potatoes fuel your workouts through complex carbs. Your muscles store energy as glycogen—think of it as your gas tank.
Empty that tank through exercise, and you feel weak. Sweet potatoes refill it so you can lift, walk, and move with strength.
The vitamin A inside keeps your immune system strong while your muscles recover.
Magnesium helps muscles contract properly and builds bone tissue. Natural anti-inflammatory compounds reduce soreness after exercise.
Bake them whole to keep nutrients intact. Roast cubed pieces at 425°F for 25 minutes. These foods for muscle mass and bone density taste great and work hard.
10. Tofu: Plant Protein with Bonus Calcium

Check the label for “calcium-set” tofu—it delivers 200-400mg of calcium per half-cup serving. Regular tofu made with other coagulants won’t give you this benefit.
The calcium-set version uses calcium sulfate, which adds significant bone-building mineral to these protein-rich foods and calcium foods.
Half a cup provides 10g of complete plant protein with all nine essential amino acids. Studies of Asian populations who eat tofu regularly show they have strong bones well into old age.
The isoflavones in tofu may help postmenopausal women keep bone density as estrogen levels drop.
Worried about soy? Current research shows moderate soy consumption is safe and beneficial for most people. The iron in tofu carries oxygen to your muscles during activity.
Tofu’s bland taste is actually perfect—it soaks up whatever flavors you cook it with. Scramble it like eggs. Cube it for stir-fries. Blend silken tofu into smoothies.
11. Whey Protein: Fast-Acting Muscle Recovery

Whey protein hits your bloodstream within 60 minutes—faster than any whole food.
One scoop typically gives you 20-25g of protein loaded with leucine, the amino acid that tells your muscles to start rebuilding.
The American College of Sports Medicine recommends getting protein within 30-60 minutes after exercise for maximum muscle repair.
Your body needs a positive nitrogen balance to keep muscle mass.
Think of nitrogen as the raw material for building muscle tissue—whey protein floods your system with it right when your muscles are screaming for fuel.
Many brands fortify whey with vitamin D and calcium, making these protein-rich foods for muscle maintenance even more powerful.
Whey isolate has more protein and less lactose than concentrate. Both work, but isolate suits people with sensitive stomachs better.
Mix it with water post-workout. Add it to oatmeal or smoothies. It’s convenient when whole food isn’t practical.

How to Combine These Foods for Maximum Benefit
Spread your protein across three meals—25-30g each time works better than eating 80g at dinner. Your muscles can only use so much protein at once. The rest gets wasted or stored as fat.
Smart pairing multiplies results. Eat salmon (vitamin D) with kale (calcium) in the same meal. Your body absorbs that calcium 30-40% better.
Add strawberries to your spinach salad—the vitamin C helps you grab more iron from those greens.
Skip coffee with your Greek yogurt breakfast. Caffeine blocks calcium absorption. Wait an hour after eating calcium-rich foods before your coffee.
Here are three powerful combinations using the best foods for strong bones and muscles:
Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with spinach, whole-grain toast, and berries Lunch: Grilled salmon over kale salad with almonds and lemon dressing
Dinner: Lean beef stir-fry with bok choy and sweet potato on the side
Pre-workout: Banana with almond butter (energy without heaviness) Post-workout: Whey protein shake within 30 minutes (fast muscle repair)

Resistance training doubles the impact of these foods for muscle mass and bone density. Lift weights twice weekly minimum.
Common Mistakes That Sabotage Your Results
Most people eat half the protein they need for maintaining muscle mass.
You need roughly 1g per pound of body weight daily—that’s 150g for a 150-pound person. Many barely hit 60g. Your muscles can’t rebuild without enough raw material.
Eighty percent of adults are vitamin D deficient. Get your levels tested with a simple blood test.
Ask your doctor for a 25-hydroxy vitamin D test. Below 30 ng/mL means you’re deficient and your bone density suffers.
Too much salt forces calcium out through your urine. Processed foods load you up with sodium. Cook at home more often to control salt intake.
Eating all your protein at dinner wastes it. Space it across three meals for constant muscle support.
Supplements can’t replace real food. Your body absorbs nutrients from salmon and eggs far better than from pills.
The myth that protein damages healthy kidneys is false—outdated science that’s been debunked repeatedly.
Conclusion:
Greek yogurt, salmon, eggs, leafy greens, lean beef, almonds, cottage cheese, sardines, sweet potatoes, tofu, and whey protein—these eleven foods protect your muscles and bones from age-related decline.
Consistency beats perfection. Eat most of these most days, and you’ll see results.

Pair this eating plan with resistance training twice weekly. The two work together, not separately. It’s never too late to start rebuilding.
Start with adding just two or three of these foods to your daily routine this week. Track how you feel after 30 days—stronger, more energetic, more confident in your body’s resilience.
Your future self, climbing stairs without hesitation and playing with grandchildren without fear of injury, will thank you for the choices you make today.
Building your arsenal of foods for muscle mass and bone density isn’t complicated, but it is powerful.

